A) Diabetes Mellitus
B) Hypertension
C) Chronic Renal Disease
A) Diabetes Mellitus (D.M.)
|
There are two major types of D.M.
i) Type I D.M (T1 D.M.) Insulin Dependent
ii) Type II D.M (T2 D.M.) Non-insulin Dependent
i) Type I D.M (T1 D.M.) (Insulin Dependent)
Type I D.M is an autoimmune disease. It affects 5 – 10% of people and usually
starts at early age. The body immune system attacks and destroys the insulin
producing cells in the pancreas.
ii) Type II D.M (T2 D.M.) (Non-insuline Dependent)
It affects 90 – 95% of people. Type II D.M. is classify into
a) Insulin deficit (Beta cell dysfunction)
b) Insulin resistance
|
 |
a) Insulin deficit – the pancreas cells do not produce insulin enough to fuel the
body cells.
b) Insulin resistance – the membranes of body’s cells are resistant to
insulin permeability.
Type II D.M usually begins in latter years and many people with type II diabetes are unaware of it. Unfortunately it is
now becoming more & more common in young people and is markedly increased in the population.
Risk factors are always associated with obesity, race, age, lack of exercise, heredity and diet (high calories & high
cholesterol, high sugar). It is a chronic degenerative disease.
Symptoms of T2 D.M.:
Thirsty, emaciation, weakness, hunger, fatigue, lethargy, impotence, lack of enthusiasm, skin pruritus……etc.
Treatment include:
1) proper diet and nutrition
2) weight control (weight loss), high fibers, low calories, low sugar, low fat
3) regular exercise, adopt healthy lifestyle habits
4) drugs include: metformin, sulphonylureas, thiazolidinediones, α-glycosidase in hibitors, glinides & insulin injection.
|
The goal of managements are:
1) To achieve and maintain optimal blood sugar levels & HbA1c below 6.5 in 6 months period.
2) To reduce cardiovascular & cerebrovascular risk factors including dyslipidaemia & hypertension.
Complication of Diabetes Mellitus are:
1) cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease (Angina, pectoris, myocardial infarction, heart attack)
2) cerebrovascular disease (C.V.A, stroke)
3) eye diseases (cataract, diabetic retinopathy, blindness)
4) renal disease (renal failure)
5) skin (chronic ulcer, diabetic foot, amputation)
6) impotence……etc.
|
.jpg) |
Type II D.M. is the major cause of premature mortality and morbidity.
To obtain a good control of blood sugar is not easy. Patients with T2 D.M should know
- The nature of the disorder
- Symptoms of Diabetes
- Risk of complication & importance of foot care
- Individual targets of treatment
- Lifestyle & meal planning
- regular exercise
- self – monitoring of blood glucose
HES Cell Polypeptides Growth Factors helps diabetes patients to reduce their blood sugar level & obtain a good control of blood sugar (HES Cell Polypeptides Nutrition regulates & nourishes endocrine system). Beside able to control blood sugar, it also corrects & improves patient general condition. The diabetic symptoms will be slowly reduced, include: thirsty, emaciation, weakness, hunger, fatigue, lack of enthusiasm…etc. It also improves sexual ability (correct impotence), wounds & ulcers are healed more easily…etc. (Increase self healing power).
B) Hypertension (Bp persistent values > 130/80 mHg
Both diabetes & hypertension are known as significant risk factors for cardiovascular & cerebrovascular disease. Therefore it is of ultimate importance. The blood pressure should be treated as aggressively as hyperglycemia in the patient of type II D.M.
|
Hypertension is divided into two categories:-
a) Primary Hypertension (Essential Hypertension)
b) Secondary Hypertension
a) Primary hypertension is not due to another underlying disease. The precise cause is unknown but a number of definite risk factors have been identified included: cigarate smoking, stress, obesity, excessive use of stimulants eg. coffee or tea, drugs abuse, high sodium intake, contraceptive, alcohol etc.
Hypertension (increase blood pressure) normally occurs in people who are overweight and also with a family history of hypertension.
b) Secondary hypertension is often associated with coronary heart disease, arteriosclerosis, kidney disorders, diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, obesity and adrenal tumors.
|
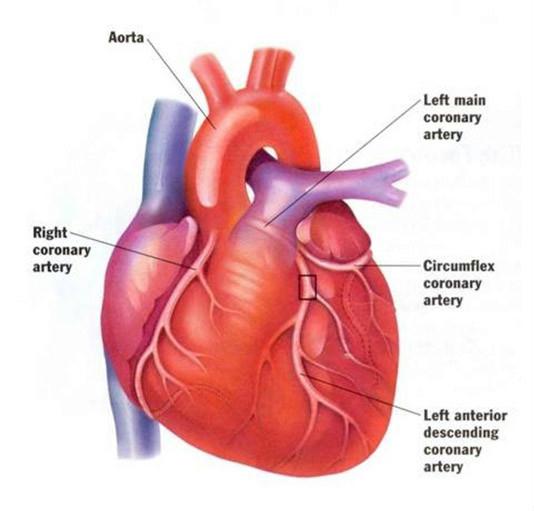 |
High blood pressure usually causes no symptoms, until complication develop. It is known as “silent killer”. Factors influence increase or decrease in blood pressure depend on activities of the nervous system and certain hormones. Increase in blood pressure, the heart must work harder to pump an adequate amount of blood to all the tissues of the body.
Warning signs associated with advanced hypertension may include headache, sweating, rapid pulse, shortness of breath, dizziness & visual disturbances.
|
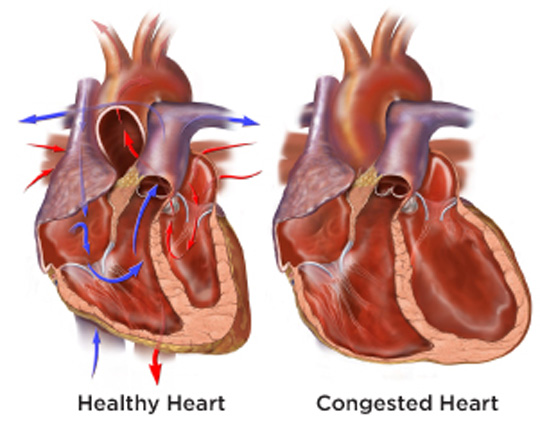
Hypertension induces
i) cardiomegaly
ii) congestive heart failure
iii) arteriosclerosis
Complications (Often associate with diabetes mellitus & dyslipidaemia )
1)cardio – vascular disease
a) micro vascular complication
b) macro vascular complication (coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease & peripheral vascular disease)
i) Coronary heart disease – myocardial infarction, heart failure
ii) Cerebrovascular disease – cerebrovascular accident (C.V.A),
a) C. thrombosis b) hemorrhage
|
 |
2)Renal disease – Arteriosclerosis, nephropathy, insufficiency, renal failure
3)eye – retina hemorrhage, blindness
Treatment:
a)Healthy life style
•Avoid all alcohol, oily food, aged cheese, aged meat, caffeine & tobacco
•Low salt diet, high fiber, plenty of fruits & vegetables
•Sufficient sleep, regular exercise
•Lowering cholesterol levels
•Check blood pressure regulary
•Weight loss
b)Medications
• Diuretics (thiazide-like)
• ACE Irihibitors
• Angiotensin II receptor blockers
• Beta – blocker
• Calcium channel blockers
HES Cell Polypeptides Nutrition enhance self healing power & regulate autonomous nervous system – sympathetic & parasympathetic nervous to obtain it balance & maintain optimal function, thus, lowering the blood pressure, relief stress & promotes blood circulation.
|
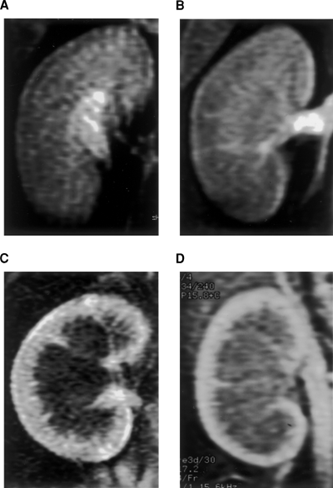
C) Chronic Renal Disease (Nephropathy)
Renal disease is a very common chronic degenerative disease.
Causes are: a) Bacteria infection (Chronic nephritis)
b) Exposure to certain drugs & toxins eg. heavy metals, solvents, pesticides, chemotherapy agents, snake or
insect venom
c) diet eg. poisonous mushroom
d) hypertension, diabetes mellitus
e) lifestyle, stress
f) can also accompany or result from many other disorders eg. congestive heart failure, chronic hypertension,
liver disease, diabetes mellitus, lupus & sickle cell anemia.
Renal disease is a “silence killer”. It is very difficult to discover in the early stage as it has no significant symptom in the early stage. A lot of patients only realize that they have renal problems after through physical examination or blood test. If waited until symptoms appear, eg. lethargy, weakness, generalize swelling, fatigue, shortness of breath, skin pruritus, anemia, loss of appetide & increase in blood pressure, it is already at late stage and not far away from renal dialysis.
|
 |
Renal problems (Renal insufficiency, renal failure or total renal failure), normally must restrict protein & salt intake. If consume large quantities of protein, the metabolic waste products have to be excreted through kidneys. This will add more stress to the defected kidneys & worsen the condition (raise in blood creatinine & BUN levels. Because of protein restriction (deficit of amino acids & polypeptides), this will affect the body’s cell metabolism & organs function.
HES Cell polypeptides Growth Factors contains vital nutrients for the body’s cells and organs and promotes normal metabolism and maintain it optimal function. It does not form metabolic wastes in the liver and adds burden to the kidney. In fact it can improve renal function and also prolong the time for renal dialysis.